Welcome to the MDos platform
MDos is a Kubernetes based application runtime platform, it's aim is to greatly simplify the process of creating, building and deploying applications on a Kubernetes cluster without compromising on security and efficiency
This documentation is for the
MDosplatform Git repository available here
MDos as a fully managed cluster stack or simply as a deployment framework
1. As a fully managed cluster and it's dependencies
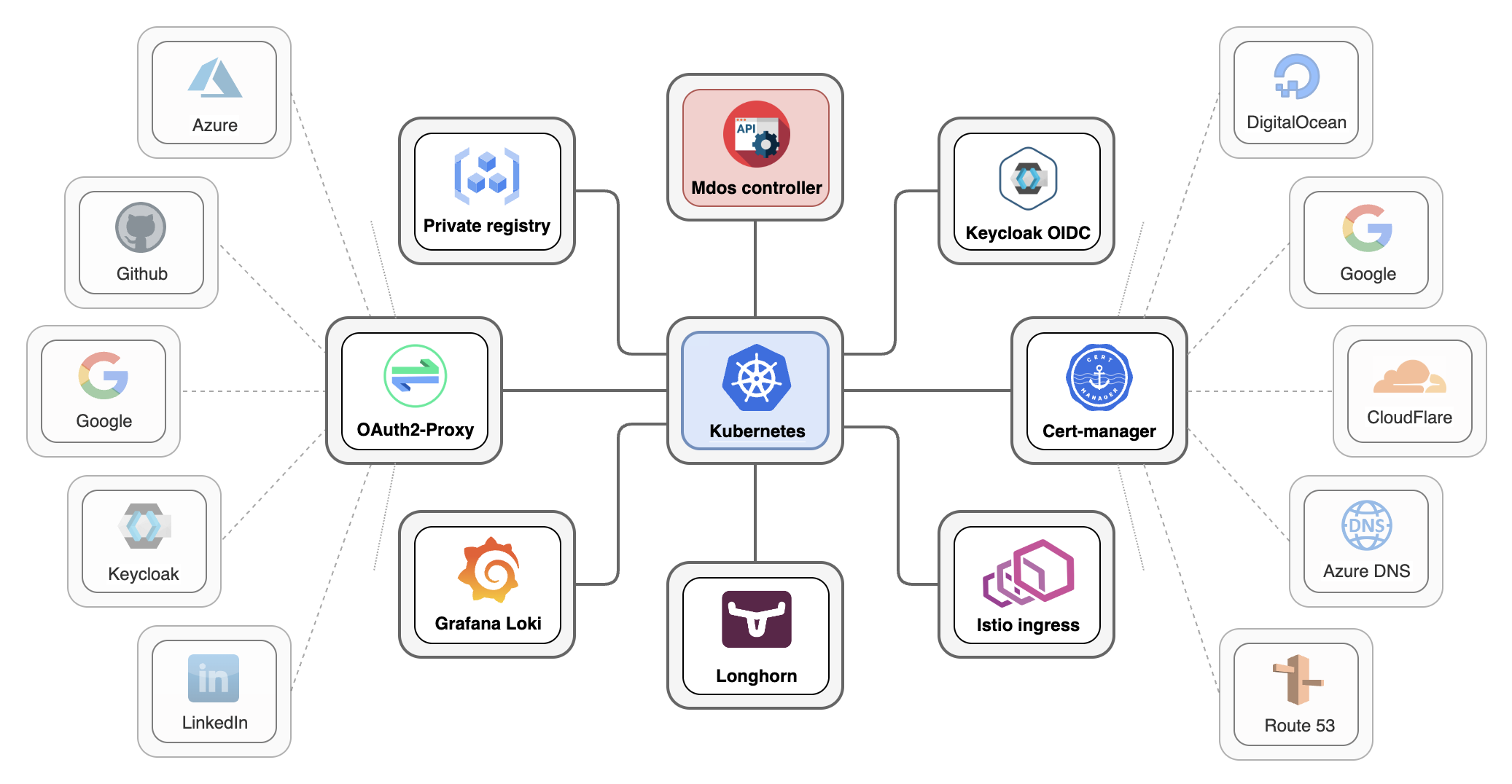 The full instance of MDos is packed with extensions and features that go beyond the basic application deployment needs. It allows you to abstract away concepts such as SSO, certificate management, multi-tenancy on one single cluster along with advanced RBAC features, a private secured registry and more. This is useful if you start from scratch and you are managing your kubernetes cluster yourself versus using a managed Kubernetes cluster such as EKS, GKE, Openshift and so on.
The full instance of MDos is packed with extensions and features that go beyond the basic application deployment needs. It allows you to abstract away concepts such as SSO, certificate management, multi-tenancy on one single cluster along with advanced RBAC features, a private secured registry and more. This is useful if you start from scratch and you are managing your kubernetes cluster yourself versus using a managed Kubernetes cluster such as EKS, GKE, Openshift and so on.
Feature request
At some point, the full MDos platform will be ported to such environments as well, but for now this is not the case. The community will drive this need, so speak up if you think this is necessary rather sooner than later.
2. And/or as an application deployment framework only (onto your own cluster)

If you are managing your own cluster, but you would like to leverage the MDos application deployment framework to manage and deploy your applications onto the cluster, then this is the mode for you.
One single and easy to understand YAML file for everything you need, no deep kubernetes knowledge needed, no scattered low level kubernetes resource yaml files and no complex resource matching patterns needed.
Managed Kubernetes Clusters such as EKS and Openshift often already come with a few integrated extensions of their own in order to leverage platform specific features such as Ingress, Certificate management and so on. What those platforms do not provide is a framework to simplify your application configuration and deployments with. Developers and devops engineers still need a very good understanding of Kubernetes artifacts and resources in order to deploy their applications onto Kubernetes. Even experienced Kubernetes folks still have to deal with allot of overhead when digging into those yaml files for some advanced use cases.
Limitations
When deploying MDos in framework only mode, you won't get advanced features such as OIDC SSO authentication, Automated certificate management, managed multi-tenancy and RBAC support or a private registry OOTB. This deployment focuses on the application framework only.
With the MDos framework & CLI, this is what a application deployment looks like for yaml config file just like the one on the left:
This will:
- Build your docker image
- Push it to the target registry
- Deploy everything on your Kubernetes cluster
- Provide you with feedback of how the deployment is going
Disclaimer
MDos is in beta stage at the moment, it is under development and should not be used in production yet. Before investing more sweat and tears into this, I want to make sure that there is interest from the community first.
Please test it, provide some feedback, or even better, join the party in developing it further.
If you encounter some miss-behavior, or if you believe something needs to be adapted, create an issue on the mdos git repo and I will come back to you shortly.
Why would you want to use it?
Let's face it, Kubernetes is great, most probably one of the best Container runtime platforms ever build with almost endless capabilities. It is no surprising that 70% of all companies use Kubernetes in production somewhere in their public / private cloud environnement.
That said, it's complexity is often a deterrent, and leads to badly designed deployment scenarios, regularly exposing security threats as well as miss-usage of certain cluster based capabilities, leading to under-utilization of it's capabilities.
Companies often end up provisioning multiple Kubernetes clusters to manage multi-tenant scenarios because properly segregating users and projects in a secure way on a single cluster can be complicated to achieve and maintain.
Other pain points faced by non kubernetes experts are plentiful:
- How do you provision your static application volume content to your Pods?
- How do you secure your applications on the network level?
- How do you implement SSO and authentication / authorization mechanisms on your applications?
- My application does not deploy on Kubernetes, I have no idea why that is and how to fix it?
- The list goes on and on...
After having worked on Kubernetes for several years now and managed teams of developers and architects that had to develop and maintain Kubernetes instances, it became clear for me that something had to change.
Companies hire developers to build applications that will run on Kubernetes, but in order to develop applications for Kubernetes, you need to have some solid experience in the domain, making you a rather experienced cloud developer with a undeniable high price tag. Unexperienced developers tend to loose allot of time on understanding Kubernetes in the first place, even more time in learning how to use it properly, leading to very expensive development cycles to get basic applications up and running.
Financially, this does not make much sense. If every company had to only hire experienced kubernetes developers to get anything done with it, project costs would rapidly spiral out of control, without mentioning the fact that there are not that many skilled kubernetes experts available in the first place.
MDos is an attempt to solve some of those complexity issues for developers and companies, letting them focus on developing applications and not about how to get them running securely on Kubernetes.
Features
Those can be split into 5 families:
- Application specific resource configurations
- Deploy and debug your applications
- Advanced volume and storage workflows
- Multi-tenant based segregation
- OIDC / OAuth2 authentication & Application RBAC
- Cert-Manager for TLS certificate issuer and secret management
1. Application specific resource configurations
Using the MDos CLI and a unified mdos.yaml application descriptor file, you can build complex Kubernetes deployment scenarios without any knowledge of Kubernetes resource definition types such as Deployments, StatefulSets, Pods, Services, PV & PVCs, VirtualServices, Secrets, ConfigMaps, NetworkPolicies ... (just to name a few)
Therefore, build your applications using higher level artefact that will translate to lower level Kubernetes resource definitions based on Kubernetes best practices.
- Scaffold a new
applicationworkspace - Scaffold a application
componentinside your mdosapplication - Add config files & environment variables to your application components
- Add secret (sensitive) files and environment variables to your application components
- Expose your application components to other resources within the cluster
- Configure hostname based ingress rules to allow access to your application components from outside of the cluster
- Mount various volume types to your application components
- ...
2. Deploy and debug your applications
- One mdos CLI command to deploy your applications and sync static volumes with your pods
- Get real-time detailed feedback on your deployments, providing valuable feedback on what might go wrong in order to fix it
- Get all application component logs, including init container logs in case of a failed deployment for instant debugging
- Aggregate all application & platform logs in Loki, accessible through a dedicated API (TODO)
3. Advanced volume and storage workflows
- Synchronize / provision static local data with your application component volumes before they start in Kubernetes
- Provision shared filesystem volumes for your application components (TODO)
4. Multi-tenant based segregation
- A tenant will get a Kubernetes namespace as well as a dedicated Keycloak client (for user management)
- You can create users on the platform and link them to one or more tenants
- Manage user permissions (RBAC) specifically for each tenant namespace / keycloak client
- Kubernetes namespaces let you take advantage of network and resource segregation mechanisms for each tenant
5. OIDC / OAuth2 authentication & Application RBAC
- Provision OIDC / OAuth2 based Authentication providers to your cluster ready to use
- Link OIDC / OAuth2 provisioned providers to your application components to protect those resources (no app changes needed)
- Assign roles to your users specifically on each tenant / keycloak client, allowing you to implement your ACL logic without having to deal with authentication at all
6. Cert-Manager for TLS certificate issuer and secret management
- Register Cert-Manager Issuers onto your cluster or namespace
- Generate and manage certificates / secrets from your Issuers